Making Best Use Of Product Top Quality With Effective Foam Control Strategies
Making Best Use Of Product Top Quality With Effective Foam Control Strategies
Blog Article
Efficient Methods for Accomplishing Optimal Foam Control in Chemical Manufacturing
Effective foam control is a vital element of chemical manufacturing that can considerably impact production performance and item top quality. By comprehending the systems of foam formation and picking ideal anti-foaming representatives, makers can take proactive actions to alleviate too much foam.
Recognizing Foam Development

Surfactants, or surface-active agents, reduce the surface area stress of the liquid, helping with bubble security and advertising foam generation. Additionally, anxiety or mixing procedures can improve bubble formation, often aggravating foam problems. The qualities of the liquid tool, including thickness and density, more impact foam behavior; for instance, more thick liquids tend to catch air better, bring about boosted foam stability.
Understanding these essential elements of foam development is vital for reliable foam control in chemical manufacturing. By acknowledging the problems that promote foam growth, manufacturers can apply targeted techniques to alleviate its adverse impacts, thereby enhancing manufacturing processes and making sure regular product top quality. This foundational understanding is essential before discovering specific techniques for managing foam in commercial settings.
Choice of Anti-Foaming Representatives
When choosing anti-foaming agents, it is important to take into consideration the specific attributes of the chemical process and the sort of foam being created (Foam Control). Numerous variables influence the effectiveness of an anti-foaming agent, including its chemical structure, temperature stability, and compatibility with various other process materials
Silicone-based anti-foams are commonly utilized as a result of their high performance and wide temperature level array. They function by lowering surface area stress, permitting the foam bubbles to integrate and damage even more conveniently. They may not be appropriate for all applications, especially those involving sensitive solutions where silicone contamination is a concern.
On the various other hand, non-silicone representatives, such as mineral oils or natural substances, can be advantageous in specific situations, especially when silicone deposits are unfavorable. These representatives have a tendency to be less effective at greater temperatures but can supply effective foam control in various other conditions.
Furthermore, comprehending the foam's beginning-- whether it develops from aeration, anxiety, or chemical reactions-- overviews the option procedure. Evaluating under actual operating problems is critical to make certain that the selected anti-foaming agent fulfills the distinct demands of the chemical production process properly.
Refine Optimization Techniques
Reliable foam control is an important facet of optimizing chemical manufacturing procedures. By fine-tuning these parameters, operators can minimize turbulence, thus decreasing foam formation during blending.
In addition, controlling temperature and stress within the system can significantly affect foam generation. Decreasing the temperature may reduce the volatility of certain parts, resulting in reduced foam. Maintaining optimal pressure degrees helps in alleviating too much gas launch, which adds to foam stability.
One more reliable method is the critical addition of anti-foaming agents at vital phases of the process. Cautious timing and dosage can make sure that these representatives effectively suppress foam without interrupting various other procedure parameters.
Additionally, integrating an organized examination of basic material homes can aid recognize pop over to this web-site inherently foaming compounds, enabling preemptive steps. Performing normal audits and process reviews can disclose ineffectiveness and areas for renovation, enabling continual optimization of foam control approaches.
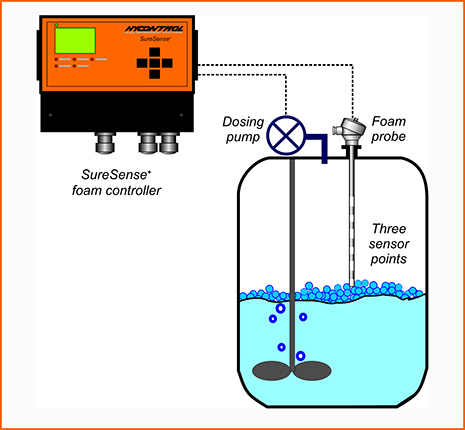
Monitoring and Control Systems
Monitoring and check out here control systems play a vital function in maintaining ideal foam management throughout the chemical production procedure. These systems are essential for real-time observation and modification of foam levels, making sure that manufacturing performance is optimized while decreasing disturbances brought on by extreme foam formation.
Advanced sensing units and instrumentation are utilized to find foam thickness and height, supplying crucial information that informs control formulas. This data-driven method enables the timely application of antifoaming agents, making sure that foam degrees remain within appropriate limitations. By incorporating tracking systems with process control software, makers can implement computerized responses to foam variations, minimizing the requirement for manual treatment and enhancing functional consistency.
Additionally, the assimilation of maker learning and anticipating analytics right into keeping track of systems can assist in aggressive foam administration. By examining historic foam data and operational specifications, these systems can anticipate foam generation patterns and advise preemptive measures. Routine calibration and maintenance of surveillance equipment are vital to guarantee accuracy and dependability in foam discovery.
Inevitably, reliable monitoring and control systems are vital for optimizing foam control, promoting safety, and improving general productivity in chemical production environments.

Situation Research Studies and Best Practices
Real-world applications of monitoring and control systems highlight the value of foam management in chemical manufacturing. A remarkable case research study includes a large pharmaceutical supplier that executed an automated foam detection system. By incorporating real-time surveillance with anticipating analytics, the facility decreased foam-related manufacturing downtime by 30%. The data-driven method permitted prompt interventions, ensuring consistent item quality and operational efficiency.
One more excellent instance originates from a petrochemical company that adopted a combination of antifoam agents and procedure optimization methods. By assessing foam generation patterns, the organization customized its antifoam dose, resulting in a 25% decrease in chemical use and considerable expense financial savings. This targeted approach that site not only lessened foam interference yet additionally improved the total stability of the manufacturing procedure.
Final Thought
To conclude, attaining ideal foam control in chemical manufacturing demands a thorough strategy encompassing the option of appropriate anti-foaming agents, implementation of process optimization strategies, and the combination of advanced monitoring systems. Regular audits and training additionally improve the effectiveness of these techniques, promoting a culture of continuous renovation. By resolving foam formation proactively, makers can considerably enhance manufacturing performance and item quality, ultimately adding to more sustainable and cost-effective procedures.
By recognizing the devices of foam formation and selecting ideal anti-foaming representatives, manufacturers can take aggressive procedures to minimize excessive foam. The features of the fluid medium, consisting of viscosity and thickness, more influence foam actions; for example, more thick fluids tend to trap air more effectively, leading to raised foam stability.
Understanding these fundamental elements of foam formation is important for efficient foam control in chemical production. By evaluating historical foam data and operational criteria, these systems can anticipate foam generation patterns and recommend preemptive procedures. Foam Control. Normal audits of foam control gauges make sure that processes continue to be maximized, while fostering a culture of proactive foam monitoring can lead to lasting renovations across the production range
Report this page